Draw a human epithelial cell and an elodea cell and delve into the fascinating world of cellular biology. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the structure and function of these two essential cell types, offering a deep understanding of their significance in both human physiology and aquatic ecosystems.
Epithelial cells, the guardians of our bodies, form protective barriers lining our organs and cavities. Elodea cells, on the other hand, are the photosynthetic powerhouses of aquatic environments, contributing to the intricate web of life beneath the water’s surface.
Introduction: Draw A Human Epithelial Cell And An Elodea Cell
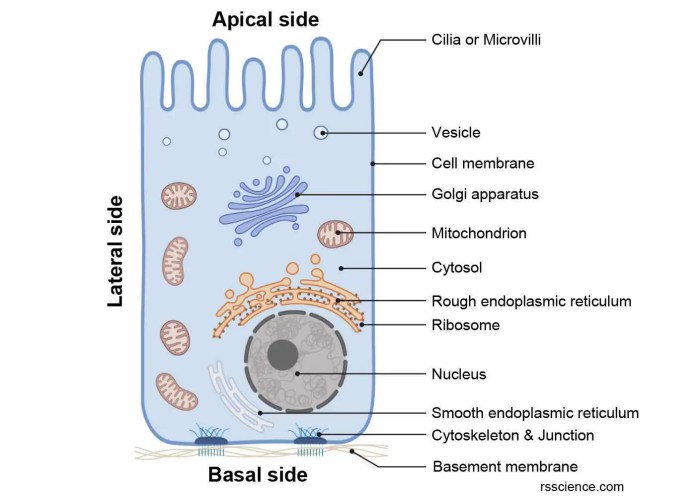
Epithelial cells are the cells that line the surfaces of organs and cavities in the human body, while elodea cells are the cells that make up the leaves of the elodea plant. Both types of cells are essential for the proper functioning of their respective organisms, and understanding their structure is key to understanding their function.
Structure of an Epithelial Cell
Epithelial cells are typically thin and flat, and they are closely packed together to form a barrier that protects the underlying tissues from the environment. The cells have a variety of organelles, including a nucleus, mitochondria, and endoplasmic reticulum. The nucleus contains the cell’s DNA, while the mitochondria produce energy.
The endoplasmic reticulum is responsible for protein synthesis.
Role of the Cell Membrane, Cytoplasm, and Nucleus
The cell membrane surrounds the cell and regulates the passage of materials into and out of the cell. The cytoplasm is the fluid-filled space inside the cell, and it contains the organelles. The nucleus is the control center of the cell, and it contains the cell’s DNA.
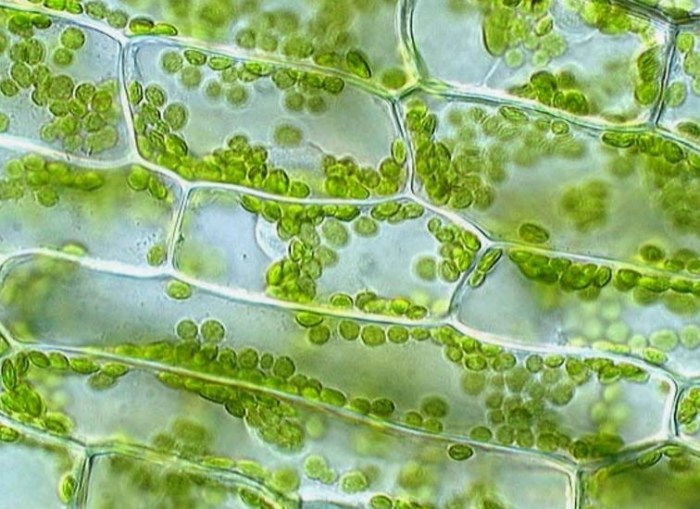
Structure of an Elodea Cell
Elodea cells are also thin and flat, but they are not as closely packed together as epithelial cells. The cells have a variety of organelles, including a nucleus, chloroplasts, and a vacuole. The nucleus contains the cell’s DNA, while the chloroplasts are responsible for photosynthesis.
The vacuole is a large, fluid-filled space that helps to maintain the cell’s shape.
Role of the Cell Wall, Chloroplasts, and Vacuole, Draw a human epithelial cell and an elodea cell
The cell wall surrounds the cell and protects it from the environment. The chloroplasts are responsible for photosynthesis, which is the process by which plants convert sunlight into energy. The vacuole helps to maintain the cell’s shape and also stores water and nutrients.
Comparison of Epithelial and Elodea Cells
| Cell Type | Shape | Organelles | Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| Epithelial | Thin and flat | Nucleus, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum | Protects underlying tissues |
| Elodea | Thin and flat | Nucleus, chloroplasts, vacuole | Photosynthesis |
Functions of Epithelial and Elodea Cells
Epithelial cells perform a variety of functions in the human body, including:
- Protection: Epithelial cells form a barrier that protects the underlying tissues from the environment.
- Secretion: Epithelial cells secrete mucus and other substances that help to protect the underlying tissues.
- Absorption: Epithelial cells absorb nutrients and other substances from the environment.
- Excretion: Epithelial cells excrete waste products from the body.
Elodea cells perform a variety of functions in the aquatic environment, including:
- Photosynthesis: Elodea cells contain chloroplasts, which are responsible for photosynthesis. Photosynthesis is the process by which plants convert sunlight into energy.
- Oxygen production: Elodea cells produce oxygen as a byproduct of photosynthesis. This oxygen is essential for the survival of other organisms in the aquatic environment.
- Carbon dioxide absorption: Elodea cells absorb carbon dioxide from the water. Carbon dioxide is a necessary ingredient for photosynthesis.
Conclusion
Epithelial cells and elodea cells are two types of cells that play essential roles in their respective organisms. Understanding the structure and function of these cells is key to understanding the functioning of the human body and the aquatic environment.
Clarifying Questions
What is the primary function of epithelial cells?
Epithelial cells primarily serve as protective barriers, lining the surfaces of organs and cavities within the human body.
How do elodea cells contribute to aquatic environments?
Elodea cells are responsible for photosynthesis, the process by which sunlight is converted into energy, providing sustenance for aquatic organisms and contributing to the overall health of aquatic ecosystems.