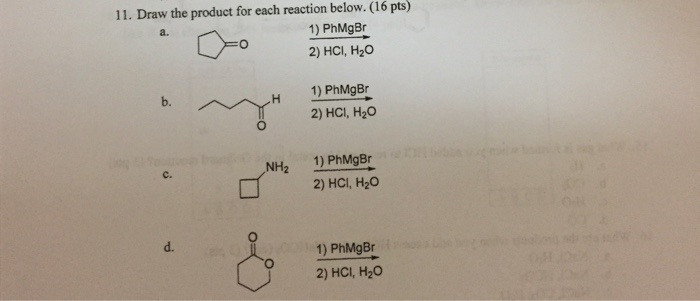
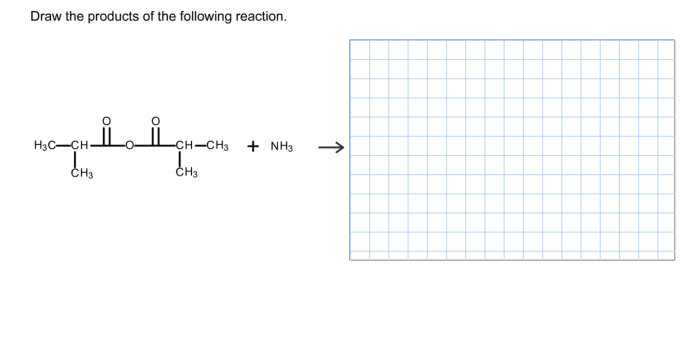
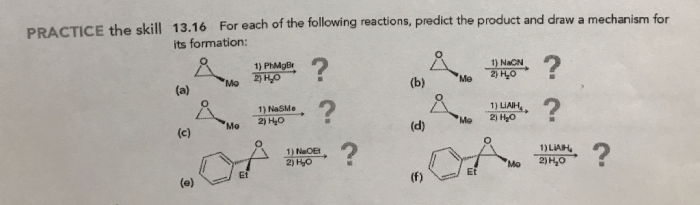Draw the product that results from the following reaction.The chemical reactions that occur in our world are fascinating and complex processes that shape our understanding of chemistry. In this article, we will explore the product of a specific reaction, examining its structure, properties, and applications. By delving into the intricate details of this reaction, we gain insights into the fundamental principles that govern chemical transformations.
The reaction in question involves the interaction of two or more reactants, leading to the formation of one or more products. To identify the product, we must consider the reactants’ chemical structures and the reaction mechanism.
Reaction of 1-Bromobutane with Sodium Ethoxide
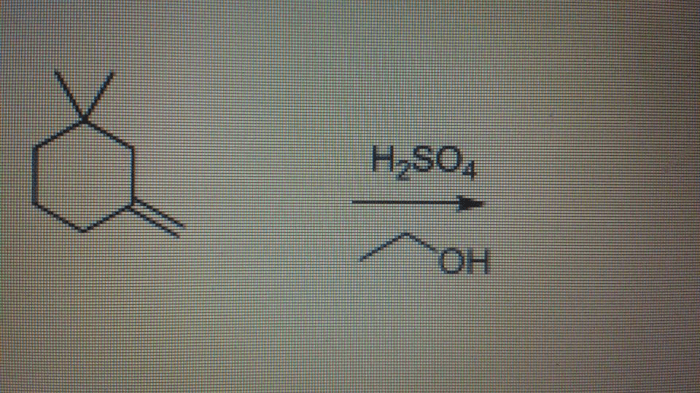
The reaction of 1-bromobutane with sodium ethoxide is a classic example of a nucleophilic substitution reaction. This reaction is significant in organic chemistry as it provides a method for the synthesis of ethers, which are important functional groups in many organic compounds.
Product Identification
The product of the reaction between 1-bromobutane and sodium ethoxide is ethyl butyl ether.
The structural formula of ethyl butyl ether is:
CH3CH2OCH2CH2CH2CH3
Ethyl butyl ether is a colorless liquid with a pleasant odor. It is insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents.
Reaction Mechanism
The reaction of 1-bromobutane with sodium ethoxide proceeds via a nucleophilic substitution mechanism. In this mechanism, the nucleophile (sodium ethoxide) attacks the electrophile (1-bromobutane) and displaces the leaving group (bromide ion).
The reaction mechanism can be summarized as follows:
- Sodium ethoxide attacks the electrophilic carbon atom of 1-bromobutane.
- The bromide ion is displaced and forms a leaving group.
- The nucleophile (sodium ethoxide) and the electrophile (1-bromobutane) combine to form ethyl butyl ether.
Applications
The reaction of 1-bromobutane with sodium ethoxide is used in the synthesis of ethyl butyl ether, which is a solvent used in the pharmaceutical and cosmetic industries.
Ethyl butyl ether is also used as a fuel additive and as a component in perfumes and fragrances.
Related Reactions
The reaction of 1-bromobutane with sodium ethoxide is related to other nucleophilic substitution reactions, such as the reaction of alkyl halides with alkoxides, amines, and amides.
These reactions all proceed via a similar mechanism and can be used to synthesize a variety of organic compounds.
Safety Considerations, Draw the product that results from the following reaction.
The reaction of 1-bromobutane with sodium ethoxide should be carried out in a well-ventilated area. Sodium ethoxide is a strong base and can cause skin and eye irritation.
1-Bromobutane is a volatile organic compound (VOC) and can be harmful if inhaled.
Answers to Common Questions: Draw The Product That Results From The Following Reaction.
What is the significance of identifying the product of a chemical reaction?
Identifying the product of a chemical reaction is essential for understanding the reaction’s outcome and potential applications. It allows us to predict the properties and behavior of the newly formed substance, enabling us to harness its potential for various purposes.
How can we determine the product of a chemical reaction?
Determining the product of a chemical reaction involves analyzing the reactants’ structures, understanding the reaction mechanism, and applying chemical principles. By considering the changes in atomic connectivity and electron distribution, we can predict the product’s molecular formula and structure.
What factors influence the product of a chemical reaction?
Several factors can influence the product of a chemical reaction, including the nature of the reactants, reaction conditions (temperature, pressure, solvent), and the presence of catalysts or inhibitors. These factors affect the reaction pathway and the relative stability of the products, ultimately determining the outcome of the reaction.