Cell size is limited by surface area worksheet answer key – Delving into the fascinating world of cell biology, we encounter the intriguing concept of cell size being limited by surface area. This fundamental principle governs the intricate balance between a cell’s physical dimensions and its ability to function effectively. Understanding this relationship is paramount in unraveling the mysteries of cellular life and its implications for various biological processes.
As we delve deeper into this topic, we will explore the challenges cells face in maintaining an optimal size, examine the role of surface area to volume ratio in cellular efficiency, and uncover the mechanisms cells employ to overcome diffusion limitations.
Additionally, we will investigate the influence of cell size on cell division and growth, highlighting the functional adaptations that enable cells to exhibit diverse sizes and perform specialized tasks.
Cell Size Limitations
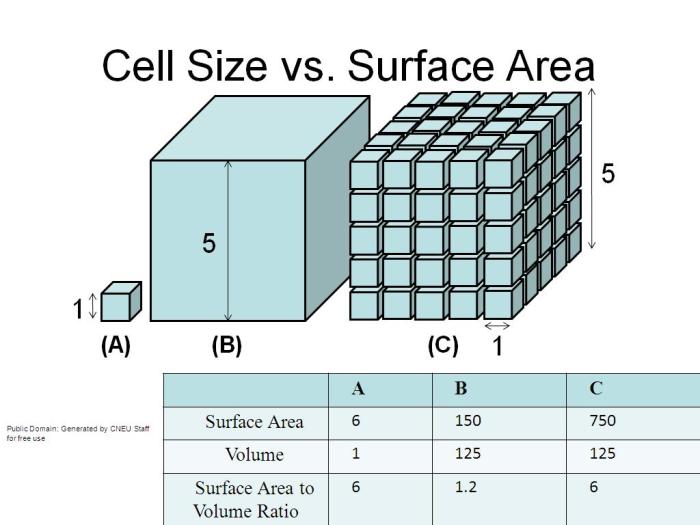
Cell size is constrained by the surface area to volume ratio. As a cell grows, its volume increases more rapidly than its surface area, limiting the cell’s ability to exchange nutrients and waste products with its environment.
Maintaining a balance between cell size and surface area is crucial for cell function. Too large a cell will have insufficient surface area to meet its metabolic demands, while too small a cell may not be able to accommodate all of its necessary organelles and structures.
For example, muscle cells are large and have a high surface area to volume ratio, allowing them to generate a lot of force. In contrast, nerve cells are long and thin, with a low surface area to volume ratio, which allows them to transmit electrical signals over long distances.
Surface Area to Volume Ratio, Cell size is limited by surface area worksheet answer key
Surface area to volume ratio is a measure of the amount of surface area available for exchange relative to the volume of the cell.
As cell size increases, the surface area to volume ratio decreases. This is because the surface area increases as the square of the cell’s radius, while the volume increases as the cube of the cell’s radius.
| Cell Size | Surface Area | Volume | Surface Area to Volume Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 μm | 4π μm2 | 4/3π μm3 | 3 μm-1 |
| 10 μm | 400π μm2 | 4000/3π μm3 | 0.3 μm-1 |
| 100 μm | 40000π μm2 | 4000000/3π μm3 | 0.03 μm-1 |
Diffusion and Transport
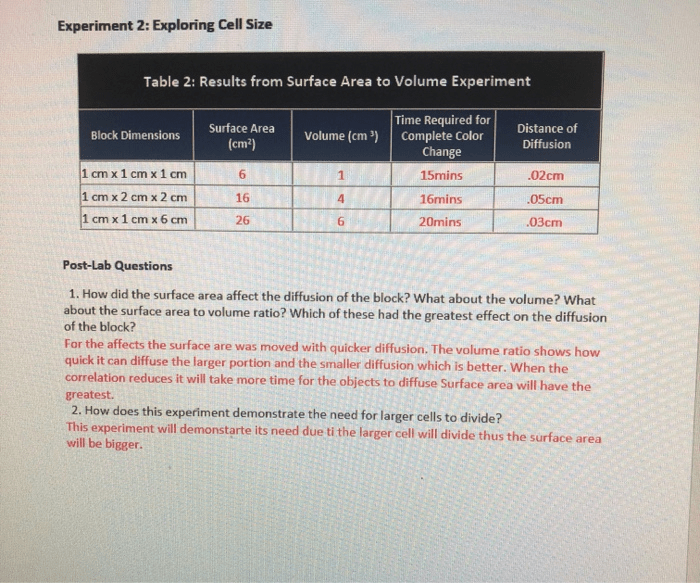
Diffusion is the movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. It is essential for cellular processes such as nutrient uptake, waste removal, and gas exchange.
Cell size affects the efficiency of diffusion. In small cells, diffusion is relatively efficient, as molecules can quickly reach the center of the cell. However, in large cells, diffusion is less efficient, as molecules must travel a longer distance to reach the center of the cell.
To overcome diffusion limitations, cells use a variety of mechanisms, such as:
- Increasing the surface area of the cell membrane
- Using membrane transporters to facilitate the movement of molecules across the cell membrane
- Creating channels within the cell to allow molecules to move more quickly
Cell Division and Growth
Cell size is closely related to cell division. Cells must reach a certain size before they can divide.
The rate of cell growth is influenced by a number of factors, including:
- The availability of nutrients
- The presence of growth factors
- The cell’s genetic makeup
Cell size affects the timing and pattern of cell division. For example, small cells tend to divide more frequently than large cells.
Examples of Cell Size Variation
Cells vary greatly in size. The smallest cells are bacteria, which are typically only a few micrometers in diameter. The largest cells are egg cells, which can be over 100 micrometers in diameter.
The functional adaptations that enable these cells to have different sizes include:
- The presence of a cell wall
- The size of the nucleus
- The number of organelles
| Cell Type | Size | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Bacteria | 1-10 μm | Carry out a wide range of metabolic processes |
| Red blood cells | 7-8 μm | Transport oxygen throughout the body |
| Muscle cells | 10-100 μm | Generate force for movement |
| Nerve cells | 10-100 μm | Transmit electrical signals |
| Egg cells | 100-150 μm | Provide nutrients for the developing embryo |
Cell Size Regulation
Cells use a variety of mechanisms to regulate their size. These mechanisms include:
- Cell cycle checkpoints
- Growth factor signaling
- Nutrient availability
Abnormal cell size regulation can lead to a number of diseases, including cancer and obesity.
FAQ Overview: Cell Size Is Limited By Surface Area Worksheet Answer Key
What is the significance of surface area to volume ratio in cell biology?
Surface area to volume ratio plays a crucial role in cellular processes as it determines the efficiency of nutrient uptake and waste removal. A larger surface area relative to volume allows for greater exchange of materials, facilitating efficient cellular function.
How does cell size affect the rate of diffusion?
Cell size inversely affects the rate of diffusion. Smaller cells have a shorter diffusion distance, allowing for faster movement of molecules across the cell membrane. Conversely, larger cells have a longer diffusion distance, which slows down the diffusion process.
What mechanisms do cells use to overcome diffusion limitations?
Cells employ various mechanisms to overcome diffusion limitations, including increasing surface area through folding or microvilli, utilizing carrier proteins to facilitate transport, and establishing specialized transport systems such as the circulatory system in multicellular organisms.